Cardiac Testing

Early detection is an integral part of treating cardiovascular disease so our patients can lead their healthiest, most fulfilling lives. At Carolina Cardiology & Vascular Associates, we utilize the industry’s most advanced technology to diagnose heart and vascular disease quickly and with more accuracy. Whether you’re looking for peace of mind or you’ve already been diagnosed with a condition, your heart deserves the best cardiovascular care. Learn more about our cardiac testing and monitoring procedures below.

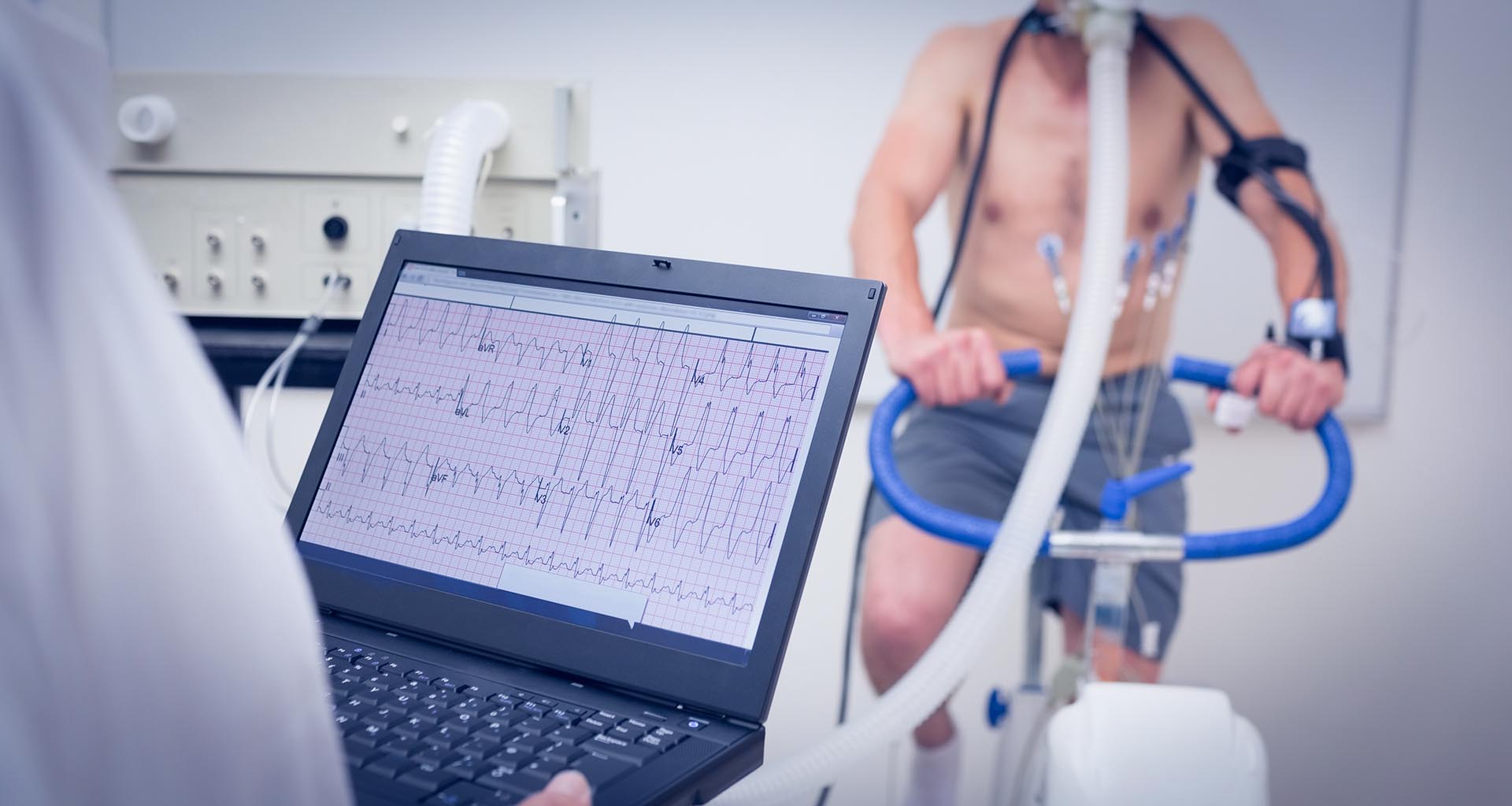
Stress Testing
Stress tests are diagnostic tools used to evaluate the heart’s ability to function during physical activity. During a stress test, patients perform some type of exercise — typically walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bicycle — while their heart is monitored. Because the heart must work harder during moments of exertion, a stress test can reveal problems with blood flow or arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat). Stress tests are also used to evaluate a patient’s level of fitness and to monitor how well treatment is working for patients who have already been diagnosed with heart disease. We perform the following stress tests at Carolina Cardiology & Vascular Associates:
Treadmill Stress Testing
To begin a traditional treadmill stress test, electrodes connected to monitoring equipment are attached to the patient’s body and a cuff is placed on the arm to check blood pressure. The patient starts walking slowly on a flat treadmill. As the test progresses, the pace and incline of the treadmill are gradually increased so the heart must work harder. The test lasts until a target heart rate is reached or the patient is unable to continue. Heart rate, blood pressure, electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) and breathing are monitored during the active part of the test and during recovery to look for abnormalities.
Nuclear Stress Testing
A nuclear stress test supplies additional information about heart function. Before the exercise phase of the test begins, a small dose of a radioactive imaging agent is administered via injection. The imaging agent emits a safe amount of radiation that can be seen with a special camera, which is used to create images of the heart at rest. The second portion of the test is a traditional treadmill stress test. When the patient’s heart rate peaks, the imaging agent is injected again and images are created of the heart during exertion. The two sets of images are compared to identify irregularities.
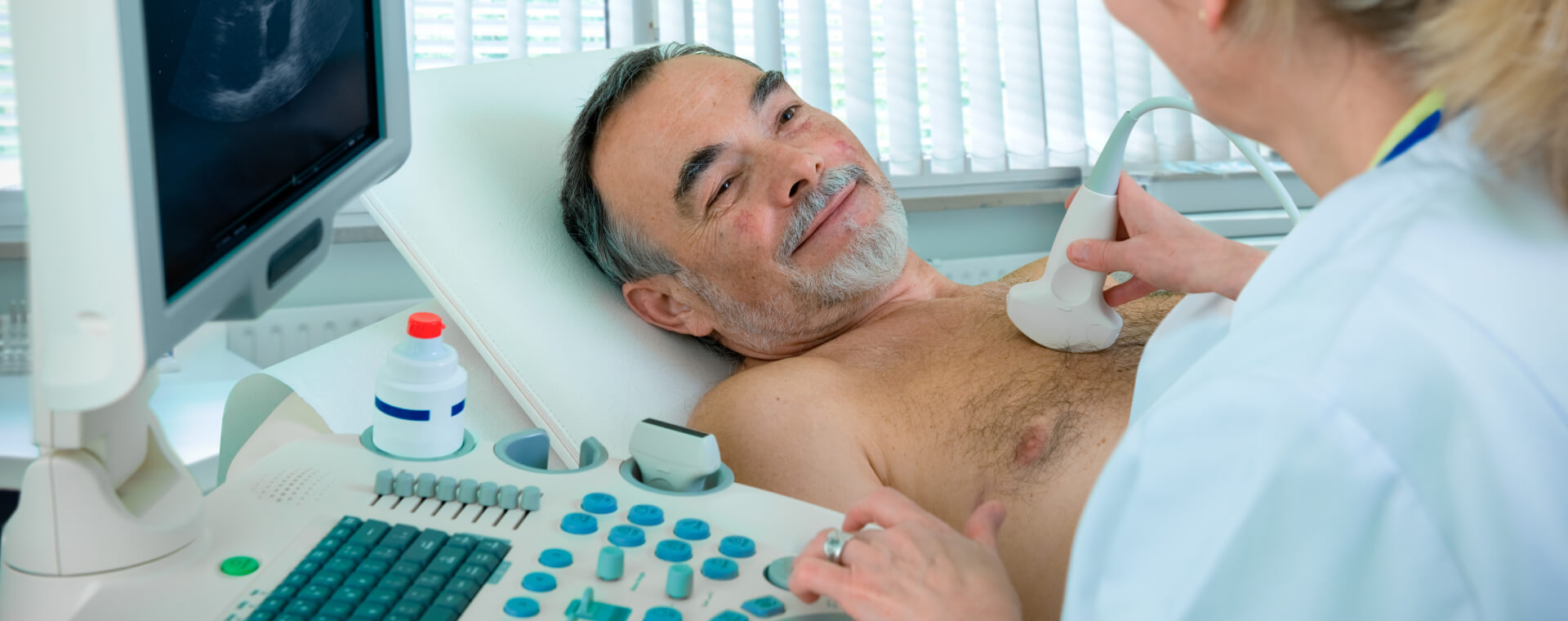
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is safe and painless technology that has numerous medical applications. Also called sonography, ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of what’s going on inside the body. An instrument called a transducer is moved across the patient’s skin while it emits high-frequency sound that is inaudible to human ears. As the sound waves bounce back, the device produces a live picture of the patient’s soft tissues and organs that is displayed on a monitor. Cardiac ultrasound is used to analyze the function of the heart and diagnose heart conditions. The ultrasound tests available at Carolina Cardiology & Vascular Associates include:
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram (echo) is an imaging study that allows doctors to evaluate the heart’s structure, function, blood flow and output to look for abnormalities. The most common type of echocardiogram is a noninvasive evaluation performed by a specially trained technologist. During the test, a gel is applied to the transducer and the device is methodically moved around the chest to provide different views of the heart. The patient may be asked to change positions or hold their breath to obtain the best quality pictures. After the images are created, they are sent to a physician for interpretation.
Carotid Artery Ultrasound
The carotid arteries are blood vessels that transport blood from the heart to the brain through the neck. They can become obstructed due to buildup of plaque, a condition called stenosis which increases the risk of stroke. A doctor may recommend a carotid artery ultrasound for patients who have medical conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, a recent transient ischemic attack (TIA) or coronary artery disease. If a significant narrowing or blockage of the carotid artery is detected, appropriate treatment may be initiated. Ultrasound is also used to monitor the state of a carotid artery after surgery to remove plaques or place a stent.
Lower Extremity Arterial and Venous Ultrasound
Lower extremity venous ultrasound may be undertaken if a doctor suspects a blood clot has formed in a vein deep in the body (deep vein thrombosis or DVT) and the patient is at risk for a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Venous ultrasound is also used to look for chronic venous insufficiency, a condition that occurs when weakened valves in the leg veins don’t allow blood to flow back to the heart. Lower extremity arterial ultrasound may be recommended for patients with symptoms of peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
Upper Extremity Arterial and Venous Ultrasound
These tests are used to evaluate the arteries and veins in the arms, wrists, shoulders and neck for possible narrowing or blockage. Though deep vein thrombosis is most common in the legs, venous ultrasound is also used to check for blood clots in the upper extremities. A doctor may recommend upper extremity vascular ultrasound if a patient has a family history of DVT or symptoms including swelling, limb pain, tenderness, discoloration or shortness of breath.

Device & Cardiac Monitoring
Advanced technology makes it possible for cardiologists to get necessary information about the heart without interrupting patients’ lives. Cardiac monitoring is used to diagnose or rule out a heart rhythm disorder and to determine the right course of treatment. A small, wearable device is worn for a prescribed period of time while it records the activity of the heart. This allows doctors to capture heartbeat abnormalities that happen infrequently and might otherwise go undetected during an office visit. Devices used for cardiac monitoring vary in terms of how they capture information and how long they can be used. Common types of cardiac monitoring include:
Pacemaker Interrogation
Pacemakers are small electronic devices that stimulate the heart with electrical impulses to restore or maintain a normal heartbeat. Pacemakers are most commonly used for patients with bradycardia (slow heartbeat), and can either be permanent (internal) or temporary (external). Patients who have a permanent pacemaker require periodic surveillance (or “interrogation”) of the implanted device. These scans evaluate the programming of the device, confirm that its components are working correctly and check the remaining lifespan of the battery. The pacemaker’s programming can be adjusted if necessary.
ICD Interrogation
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) are devices that monitor heartbeat and suppress heart arrhythmias. ICDs deliver a strong electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal heartbeat when the device senses a life-threatening change in the heart’s rhythm. After an ICD system is implanted, monitoring of the device can be done during scheduled in-office visits. These appointments are used to retrieve information from the ICD and make adjustments to its programming. ICDs may be recommended for patients who are at risk for sudden death from ventricular arrhythmias.
Remote Cardiac Monitoring
In some cases, remote monitoring can be used to observe an implanted pacemaker or ICD. Remote monitoring allows a doctor to confirm the device is functioning correctly and obtain information from the device on an as-needed basis without the patient having to travel to the office for an in-person interrogation. This is a more convenient and efficient option for many physicians and patients.

What Happens If Something Is Detected?
The results of a cardiac test could reveal a blood clot, irregular heart rhythms, narrowing of a vein or artery, structural defects of the heart or venous insufficiency, or indicate a patient is at higher risk of heart attack or stroke. If something is detected on your test, there are steps you can take to improve your health and lower your risk for worsening heart disease. Lifestyle changes, such as exercise, a healthier diet and smoking cessation, can help you manage symptoms. Medications may be prescribed if necessary. In advanced cases, a medical procedure or surgery may be considered to restore normal blood flow to the heart.
Expert Cardiac Care in South Carolina
From stress tests to ultrasound exams, testing is a critical component in the management of all forms of cardiovascular disease. These tests give your cardiologist valuable insight into the health of your heart, as well as clues to potential issues that could arise if left untreated. Dr. Dan Bouknight and his team aim to provide the highest quality cardiovascular care in the Midlands of South Carolina. If you are interested in exploring your cardiac testing options in West Columbia, we invite you to contact us at (803) 888-2282 to schedule a consultation.
Schedule Consultation
Schedule Consultation
Call us at (803) 888-2282 or fill out the form below to schedule a consultation with us!
[gravityforms id="1" title="false" description="false" ajax="true"]